
5. The most acidic compound in the followi... Organic Chemistry
Example \(\PageIndex{1}\): Acidic Groups. Using the pK a table, estimate pK a values for the most acidic group on the compounds below, and draw the structure of the conjugate base that results when this group donates a proton. Use the pKa table above and/or from the Reference Tables.. Answer. a. The most acidic group is the protonated amine, pKa ~ 5-9
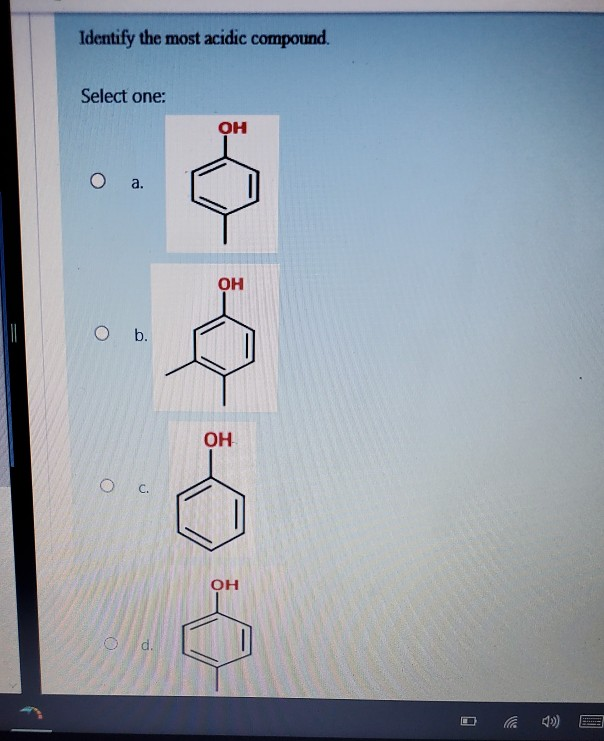
Solved Identify the most acidic compound. Select one OH а.
The correct answer to the increasing order of the acidic strengths of the given compounds is - HCOOH > CH₃COOH > CH₃CH₂COOH and so on The strengths of the carboxylic acids are known to vary based on the total power to withdraw electrons of the atoms that are bonded to the carboxyl group.

The most acidic compound among the following is
11.10: Identifying Acidic Protons. The most general principle ruling acid strength can be stated thus: strong acids have relatively stable conjugate bases. In general, the more stable the conjugate base, the stronger the acid. An important thing to remember is that stability and reactivity are inverse. The more stable a substance is, the less.
/common-acids-and-chemical-structures-603645_FINAL-54e6b0b3351b49dbb6cef54fd4817404.png)
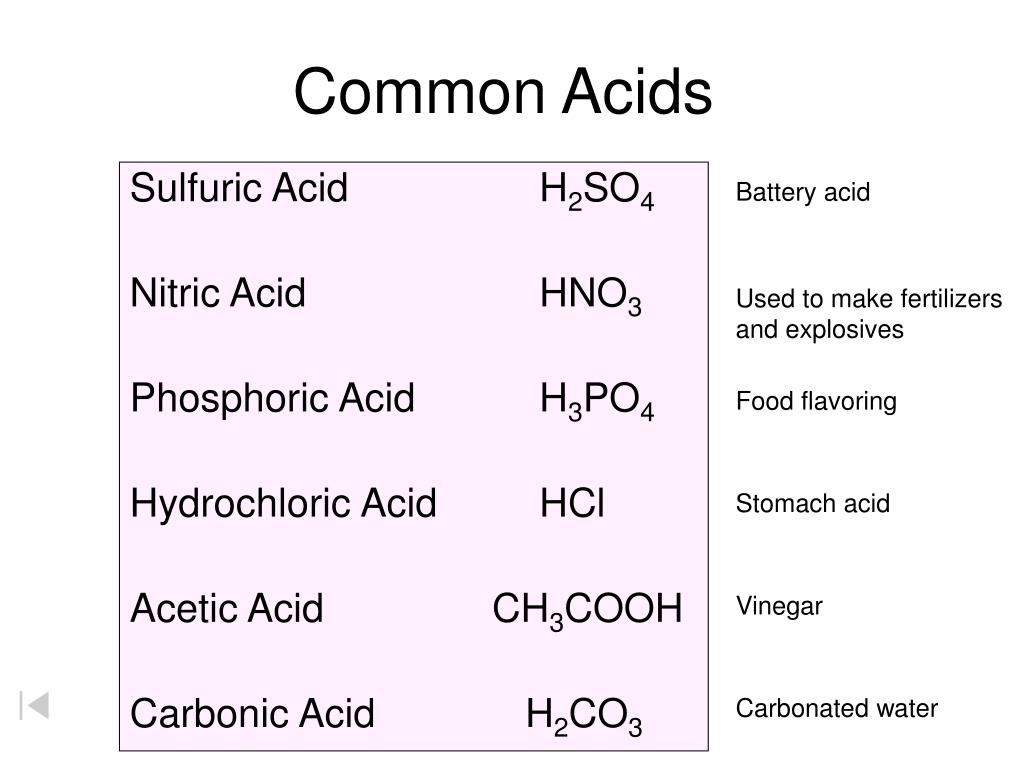
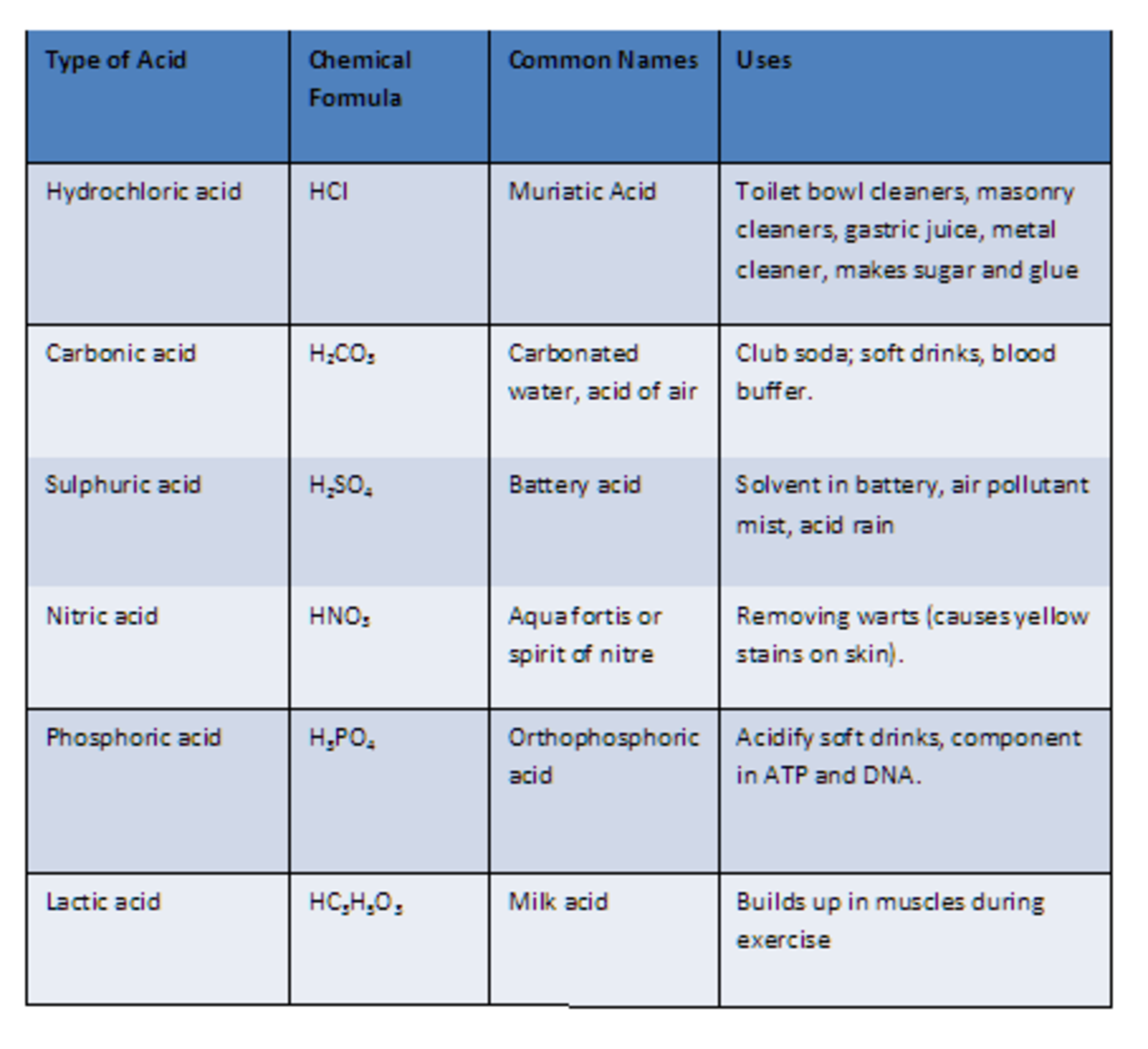
10 Common Acids and Chemical Structures
1. Factor #1 - Charge. Removal of a proton, H+ , decreases the formal charge on an atom or molecule by one unit. This is, of course, easiest to do when an atom bears a charge of +1 in the first place, and becomes progressively more difficult as the overall charge becomes negative. The acidity trends reflect this:

Which one of the following compounds is most acidic?
Rank the compounds below from most acidic to least acidic, and explain your reasoning. This page titled 7.4: Structural Effects on Acidity and Basicity is shared under a CC BY-NC-SA 4.0 license and was authored, remixed, and/or curated by Tim Soderberg via source content that was edited to the style and standards of the LibreTexts platform; a.

How to Find the Most Acidic Proton in a Molecule
Here is a list of ten common acids with chemical structures. Acids are compounds that dissociate in water to donate hydrogen ions/protons or to accept electrons . 01 of 11 Acetic Acid Acetic acid is also known as ethanoic acid. LAGUNA DESIGN / Getty Images Acetic Acid: HC 2 H 3 O 2 Also known as: ethanoic acid, CH3COOH, AcOH.

Solved Identify the most acidic compound in this series ??
For now, the concept is applied only to the influence of atomic radius on anion stability. Because fluoride is the least stable (most basic) of the halide conjugate bases, HF is the least acidic of the haloacids, only slightly stronger than acetic acid. HI, with a pK a of about -9, is one the strongest acids known.
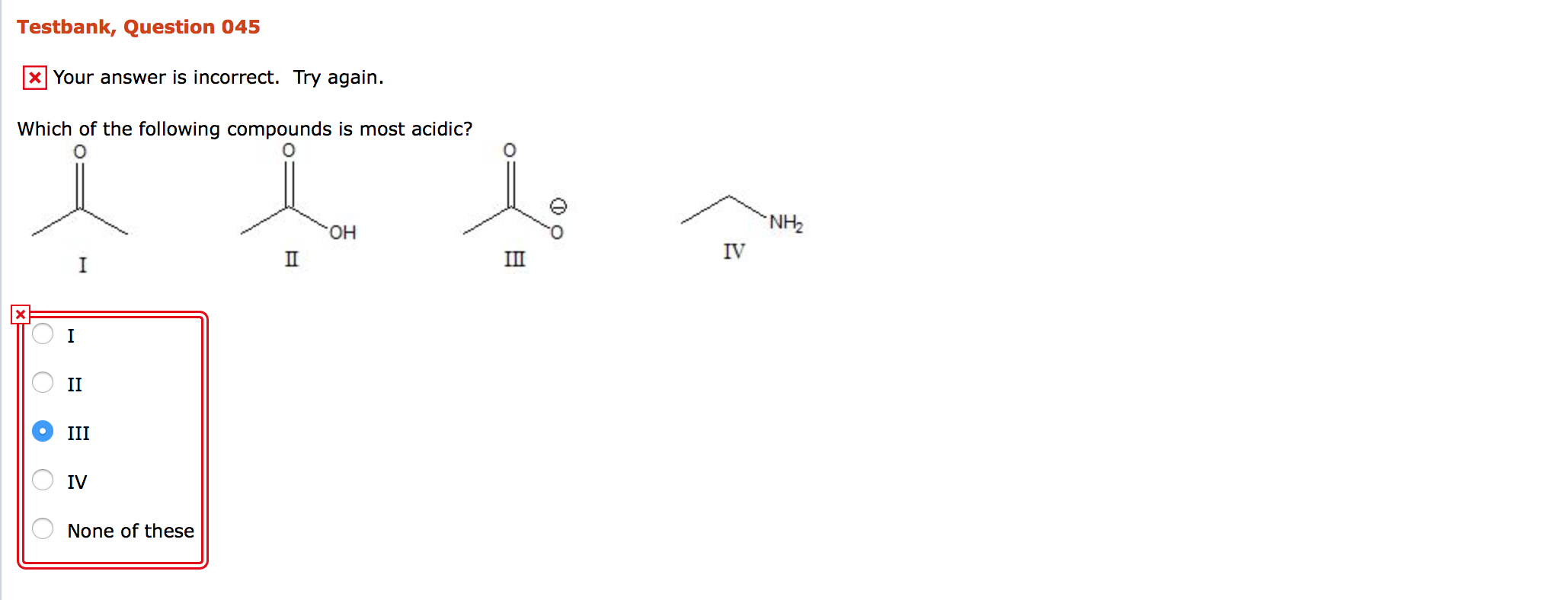
Solved Which of the following compounds is most acidic? I
The least acidic compound (second from the right) has no phenol group at all - aldehydes are not acidic. The most acidic compound (second from the left) is a phenol with an aldehyde in the 2 ( ortho ) position, and as a consequence the negative charge on the conjugate base can be delocalized to both oxygen atoms.
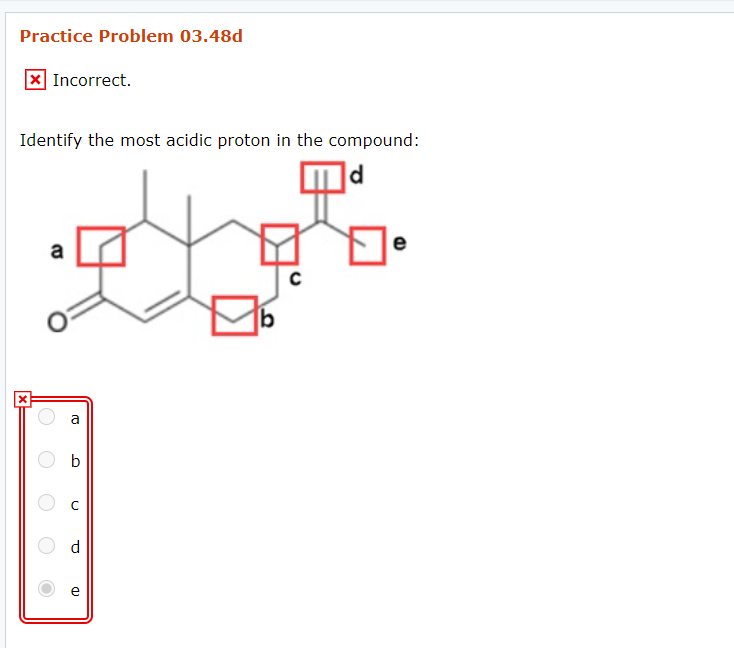
Identify the Most Acidic Proton in the Compound JohannahasBolton
Positively charged molecules, or ions, are more acidic than neutral ones. Negatively charged ions tend to be basic. Examine the periodic table of elements to figure out the strength of the electronegativity. The further to the right on the periodic table the element bonded to the hydrogen is, the stronger the acid it makes.

OneClass Identify the most acidic proton on the following compound. A) Ha B) Hb C) Hc D) Hd E
HI, with a pK a of about -9, is one the strongest acids known. More importantly to the study of biological organic chemistry, this trend tells us that thiols are more acidic than alcohols.
PPT Common Acids PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID4697679
Acidic nature of organic compounds can be commented on the basis of stability of the resulting conjugate base . If the conjugate base thus formed is stable then the compound is more acidic or the hydrogen is more acidic and vice versa. For option A we can see there is only one acidic hydrogen ie the hydrogen connected to the oxygen atom.

Among the following compound , the most acidic is YouTube
Carbonic acid is a chemical compound with the chemical formula H2CO3 H 2 CO 3 and is also a name sometimes given to solutions of carbon dioxide in water (carbonated water), because such solutions contain small amounts of H2CO3(aq) H 2 CO 3 ( aq). Carbonic acid, which is a weak acid, forms two kinds of salts: the carbonates and the bicarbonates.

Select the structure with CORRECT numbering in the chain
The world's strongest superacid is fluoroantimonic acid, HSbF 6. It is formed by mixing hydrogen fluoride (HF) and antimony pentafluoride (SbF 5 ). Various mixtures produce the superacid, but mixing equal ratios of the two acids produces the strongest superacid known to man. Properties of Fluoroantimonic Acid Superacid
Chemical Nomenclature and Chemical Formulas Owlcation
The most acidic functional group usually is holding the most acidic H in the entire molecule. "Scan and rank" sounds simple, but it conceals several difficulties that are elaborated below. Scan a molecule for known acidic functional groups . Acidic protons are usually bound to O or N. Therefore, the first step is to look for all OH and NH bonds.
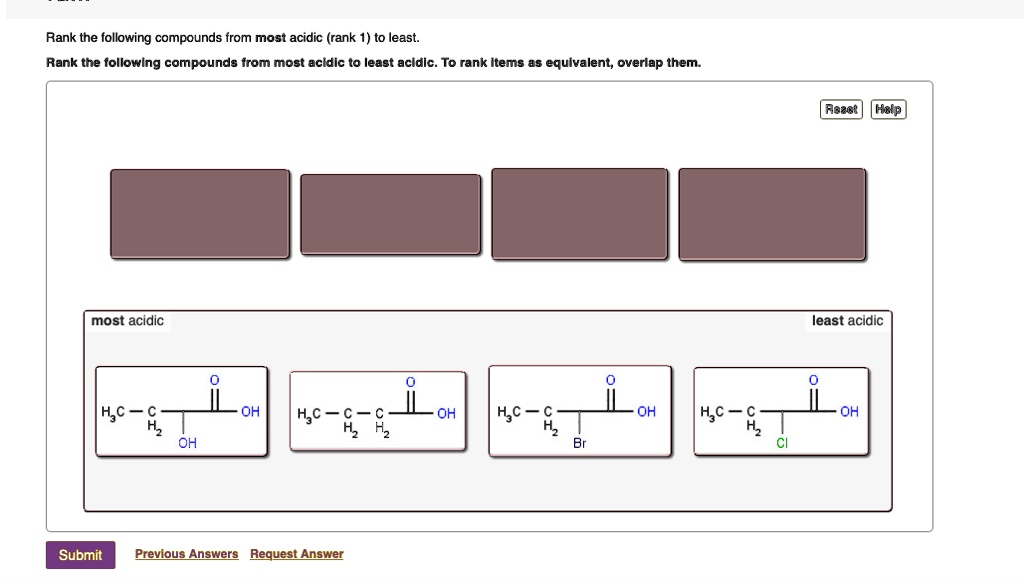
Rank the following compounds from most acidic (rank 1… SolvedLib
Tutorials Acids and Bases - How to Determine Which Acid is Stronger By Mark Coster December 1, 2021 One of the most common questions in organic chemistry is 'which of these two compounds is more acidic?' Here are the 4 most important factors to consider. How to determine the stronger acid

Chemical Nomenclature and Chemical Formulas Owlcation
Rank the compounds below from most acidic to least acidic, and explain your reasoning. (CC-NC-SA; Timothy Soderberg via UMn Morris Digital Well) Inductive Effects. The inductive effect is an experimentally observed effect of the transmission of charge through a chain of atoms in a molecule, resulting in a permanent dipole in a bond. Inductive.